Bermuda

Capital city: Hamilton
Population: 62,058 (2021)
Land area: 53.2 km²
Official language: English
Legal system: English common law
Time zone: UTC-3
Currency: Bermuda Dollar (BMD)
GDP: 7.484 USD billion (2019)
Main industries: International Business, tourism, light manufacturing
Principal exports: special purpose vehicles, alcoholic beverages including liqueurs, trailers, camping items including tents, aircraft parts, pleasure or sports vessels
Bermuda is a self-governing British overseas territory in the North Atlantic Ocean, consisting of an archipelago of 138 coral islands. It’s off the coast of the United States. It has one of the world’s most prosperous economies thanks to its offshore finance industry. Stunning beaches, golf courses, colonial architecture, and subtropical climate make it a popular tourist destination.
Although Bermuda is not a member state, it has become part of the Commonwealth family through the British Association. Therefore, Bermuda can be proud of its contribution to the Commonwealth, whether through democracy, the rule of law, sports, education, culture, and the promotion of peace and security around the world. Bermuda is an active member of the Commonwealth family of nations. The territory’s MPs are active members of the Commonwealth Parliamentary Association and support the judiciary’s responsibility in protecting justice and the rule of law.
Demographics
Native-born residents make up the majority of the population. Approximately 64% of the population was born in Bermuda. Over half of the population is black including anyone with a mix of black, white, and indigenous backgrounds. Other ethnic groups in Bermuda include whites, Asians, and people of two or more races. The official language is English, although colloquially Bermudian English is spoken, which is a combination of West Indian, American, and British English characteristics. Portuguese is still spoken and preserved in some Portuguese homes. Multiple different religions are practiced in Bermuda, the largest of which is Protestant Christianity which is the religion of over 46% of the population. Other religions include Islam, Catholicism. Some population of Bermuda are also Jehovah’s Witnesses.
History
First discovered in the early 1500s by Spanish ship captain Juan de Bermudez, Bermuda was not settled until 1609, when the British ship the Sea Venture was wrecked on the reef off Bermuda’s coasts on its way to Jamestown, Virginia. Three survivors left behind, despite the fact that the majority of survivors managed to continue toward their destination. Bermuda became a British territory three years later, and it has since been renamed Bermuda. Following the outbreak of the English Civil War in 1649, the Bermudian Civil War started. When the Somers Isles Company was dissolute the Bermudians quickly left agriculture for shipbuilding and planted the island with native juniper. The Royal Navy expanded the harbors and built a massive dockyard on Ireland Island after the American Revolution ended.
Legal System and Government
Bermuda’s legal system is based on the English and Wales common law legal system, as well as rulings of the English Court of Appeal and House of Lords are highly persuasive authority in Bermuda’s courts. Bermuda’s laws are enacted by the Bermuda Legislature. Certain UK Acts, on the other hand, apply to Bermuda to the extent that they have been specifically extended to Bermuda or have survived since they were first become Bermuda law. The court system in Bermuda comprises the Magistrates’ Court, the Supreme Court, the Court of Appeal, the Judicial Committee of the Privy Council in London (in ascending order of superiority). Bermuda’s law is heavily influenced by British law, both statute and common law (case decisions). While Bermuda’s courts will consider any reasoned judgement from a Commonwealth country, the Supreme Court of England and Wales decisions are accorded significantly more weight in the interpretation of Bermuda’s laws.
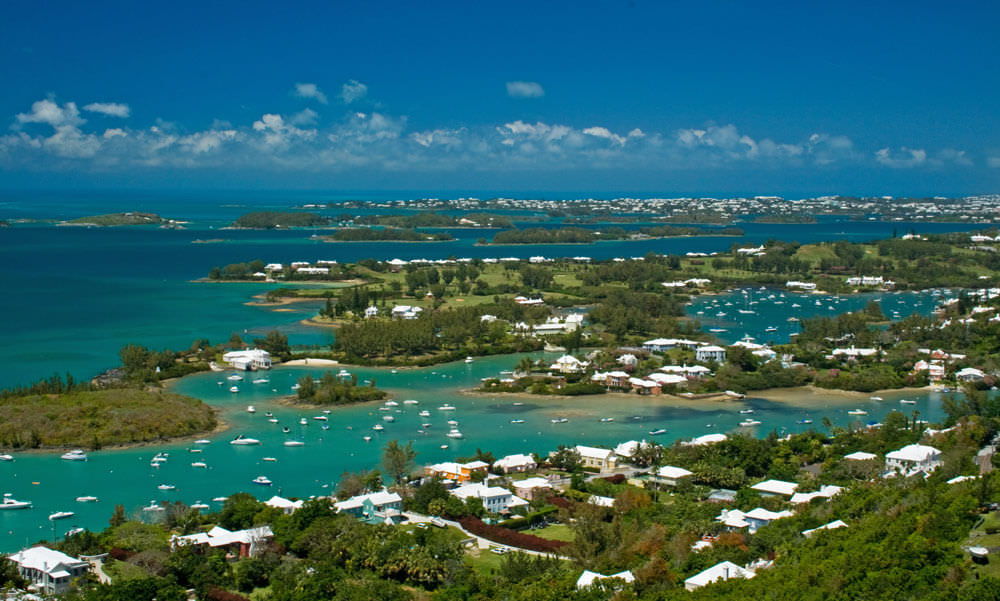

Economy
International business including insurance and financial services forms the bedrock of Bermuda’s economy, accounting for roughly 85% of the island’s GDP consistently. Most of its revenue comes from being an International Business center or offshore jurisdiction. As a premier offshore financial centre, Bermuda has no taxes on profits, income, dividends, or capital gains, has no limit on the accumulation of profit, and has no requirement to distribute dividends on this island. Tourism is Bermuda’s second-largest industry, accounting for around 5% of GDP but employing a far larger number of people. The United States brings more visitors to Bermuda than all other countries combined, accounting for around 85 percent of all visitors. Next are Canada and UK, with about 5% each, then other countries.
Trade
Bermuda’s main exports include planes, helicopters, and/or Spacecraft ($465 million), petroleum gas ($28.6 million), passenger and cargo ships ($24.4 million), recreational boats ($12.2 million), and specialized vehicles ($9.87 million). In 2019, Bermuda exported $574 million worth of good, making it the world’s number 165 exporter. Bermuda’s exports have increased by $520 million in the last five reported years, from $54.1 million in 2014 to $574 million. Most of the goods are exported to countries including Ireland ($436 million), Spain ($30.1 million), Poland ($24.5 million), United States ($24.2 million), and Pakistan ($21.8 million).
Investment Opportunities
Bermuda maintains a well-developed center for aircraft and shipping registration, finance, and management. Private jets, commercial aircraft, superyachts, and all classes of marine vessels make use of the island’s experienced corporate environment for their businesses. The Bermuda Civil Aviation Authority (BCAA) operates the 10th largest aircraft registry in the world, which both private and commercial aircraft operated under the Article 83 bis agreement
Bermuda has been a forefront “all in one” destination for investment fund structures and services since the 1970s including mutual funds and alternative funds such as hedge funds, fund-of-funds, private-equity vehicles, and innovative insurance-linked structures.
Sources
https://globaledge.msu.edu/countries/bermuda
https://www.bbc.com/news/world-latin-america-20158216
https://www.britannica.com/place/Bermuda
https://worldpopulationreview.com/countries/bermuda-population
https://www.countryreports.org/country/Bermuda/economy.htm
http://www.bermuda-online.org/economy.htm
https://taxsummaries.pwc.com/bermuda/corporate/taxes-on-corporate-income
https://www.gov.uk/government/news/commonwealth-day-in-bermuda
https://assets.kpmg/content/dam/kpmg/bm/pdf/2017/06/ACBDA-Investors.pdf